ALSR: An Adaptive Label Screening and Relearning Approach for Interval-Oriented Anomaly Detection
本文最后更新于:2 年前
Introduction
本文针对面向区间的KPI异常检测提出了Label Screening方法和Relearning Algorithm.
Contribution
- 提出了一种Label Screening方法来对区间内不同重要性进行过滤
- 提出了一种Relearning Algorithm来对FP和TP进行Relearning,在不减少Recall的条件下增大Precision
Methodology
Overall Structure
算法的整体框架如下:
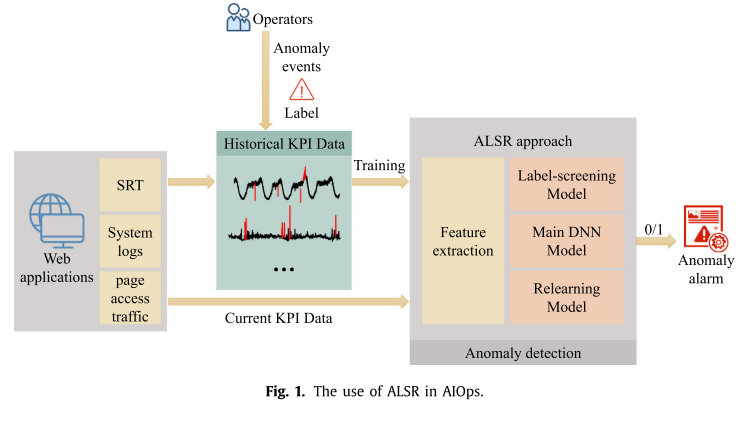
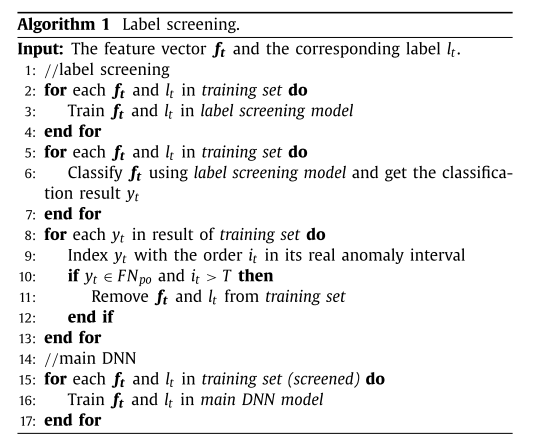
Label Screening Model
预训练的结果被分为\(TP_{po},FP_{po},TN_{po},FN_{po}\)四类,\(TP_{po}\)和\(FN_{po}\)可以被细分如下: \[ \begin{align}TP_{po}&=TP_{po,withinT}+TP_{po,afterT}\\&=TP_{po,withinT}+TP_{po,afterT,tpl}+TP_{po,after,fnl}\end{align} \]
\[ \begin{align}FN_{po}&=FN_{po,withinT}+FN_{po,afterT}\\&=FN_{po,withinT,tpl}+FN_{po,,withinT,fnl}+FN_{po,afterT,tpl}+FN_{po,afterT,fnl}\end{align} \]
其中下标\({}_{withinT}\)代表在异常片段第一个点\(T\)距离内的所有点,下标\({}_{afterT}\)代表\(T\)距离之后。下标\({}_{tpl}\)和\({}_{fnl}\)分别代表在异常片段中,包含和不包含\(TP_{po,withinT}\)的点。
以TP为例,Point-based的TP包含了在T范围之内的(即在Interval-based的标准中也会被认为是TP的点)和T范围之外的点(即在Interval-based的标准中不认为是TP的点)。而在T范围之外的点又可以细分为该异常片段是否包含\(TP_{po,withinT}\)的点(即该点在Interval-based的标准中不会被判定为TP,但该异常片段有其点会被判定为TP)。
类似的,\(TP_{io}\)和\(FN_{io}\)可以被分解为: \[ \begin{align}TP_{io}&=TP_{po,withinT}+TP_{po,afterT,tpl}+FN_{po,withinT,tpl}+FN_{po,afterT,tpl}\\&=TP_{po}+FN_{po,withinT,tpl}+FN_{po,afterT,tpl}-TP_{po,afterT,fnl}\end{align} \]
\[ \begin{align}FN_{io}&=FN_{po,withinT,fnl}+FN_{po,afterT,fnl}+TP_{po,afterT,fnl}\\&=FN_{po}+TP_{po,afterT,fnl}-FN_{po,withinT,tpl}-FN_{po,afterT,tpl}\end{align} \]
文中对该部分的分析可以分为以下几点:
- 在Interval-oriented的标准中,\(FN_{po,tpl}\)的点仍会被认为是\(TP_{io}\),而\(TP_{po,afterT}\)(不带\({}_{tpl}\))不会被认为是\(TP_{io}\),所以最终\(TP_{io}\)由所有\(TP_{po}\)加上那些会被认为是\(TP_{io}\)的\(FN_{po,tpl}\)再去掉不带\({}_{tpl}\)的\(TP_{po,afterT}\)组成,即公式(6)
- 同时,根据公式(6),如果\(TP_{po}\)变为\(FN_{po,tpl}\),也不会对最终结果造成影响。但是根据公式(5)和公式(7),\(TP_{po,withinT}\)变成\(FN_{po,withinT,fnl}\)会减小\(TP_{io}\)同时增大\(FN_{io}\)
- 文章指出,虽然\(FN_{po,withinT,tpl}\)和\(FN_{po,afterT,tpl}\)最后都会被认为是\(TP_{io}\),但作者假设\(FN_{po,withinT,tpl}\)更难检测,所以应该保留,而\(FN_{po,afterT,tpl}\)应该削减
- Label Screening方法去除了\(FN_{po,afterT}\)的点
- Screened之后的训练集被用来训练DNN主模型,但Label Screening的预测结果也会被保留,和DNN主模型的结果进行组合
算法流程如下:
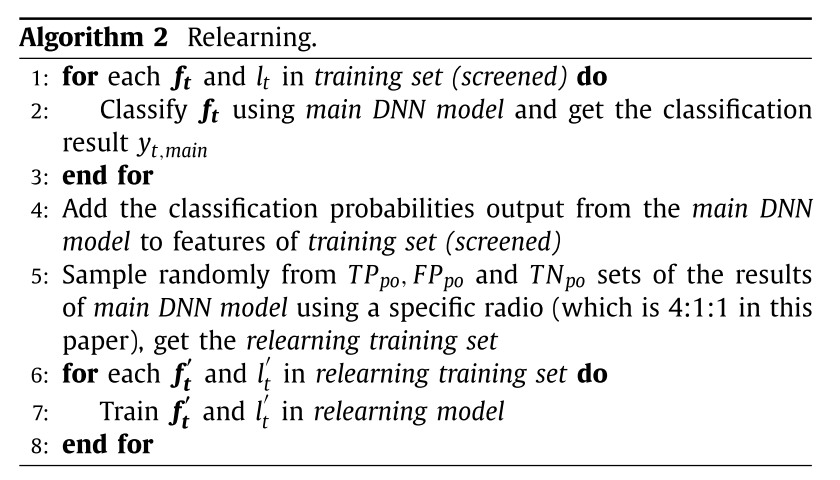
Relearning Algorithm
Relearning Model的输入是DNN主模型预测出来的异常,其中包括TP和FP。Relearning Model采用的是随机森林,其输入的样本通过采样得到: \[ \begin{align} \text{relearning}\space&\text{training set}=\\& shuffle\{4C\ast\text{randomof}(TP_{po})\\&+C\cdot\text{randomof}(FP_{po})+C\cdot\text{randomof}(TN_{po})\} \end{align} \] 其中\(C\)为常数。TN和FP都看作是负例(正常样本),TP看作是正例。
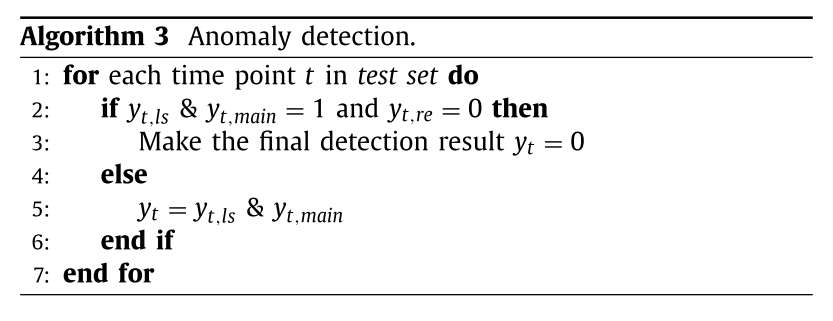
Detection
对于一个滑动窗口\(x_t=\{x_{t-w+1},\cdots,x_t\}\),异常检测算法的目标是输出检测结果\(y_t\in\{0,1\}\)来表示时间\(t\)是否发生异常。实际上算法输出的是\(p_{y_t}\in[0,1]\)概率值来表示在时间\(t\)发生异常的概率。文中三个模型会得到三个输出:\(y_{t,ls},y_{t,main},y_{t,re}\)。最终结果为: \[ y_t=y_{t,ls}\space\&\space y_{t,main}\space\& \space y_{t,re} \] 在绘制PR曲线时,采用的公式为: \[ \begin{align} p_{y_t}(th)=&(1-sig(p_{y_t,ls},th))\cdot(p_{y_t,ls})\\ &+sig(p_{y_t,ls},th)\cdot(1-sig(p_{y_t,main},th))\cdot p_{y_t,main}\\ &+sig(p_{y_t,ls},th)\cdot sig(p_{y_t,main},th)\cdot p_{y_t,re}\\ \end{align} \]
\[ y_t(th)=sig(p_{y_t}(th),th) \]
算法流程如下:
Experiments
Datasets
清华AIOps数据集,选取了25条KPI。
Preprocessing
- Missing Data. 去除。
- Standardization. Minmax Standardization,Feature Extraction使用的是Standardization后的数据。
- Feature Extraction. 使用了12种特征。
| Group | Feature Name |
|---|---|
| Values | The original values standardized |
| Statistical Features | Mean, Standard Deviation, Range, Difference... |
| Fitting Features | EWMA, AR |
| Wavelet Features | Db2 wavelet decomposition |
Results
AUCPR
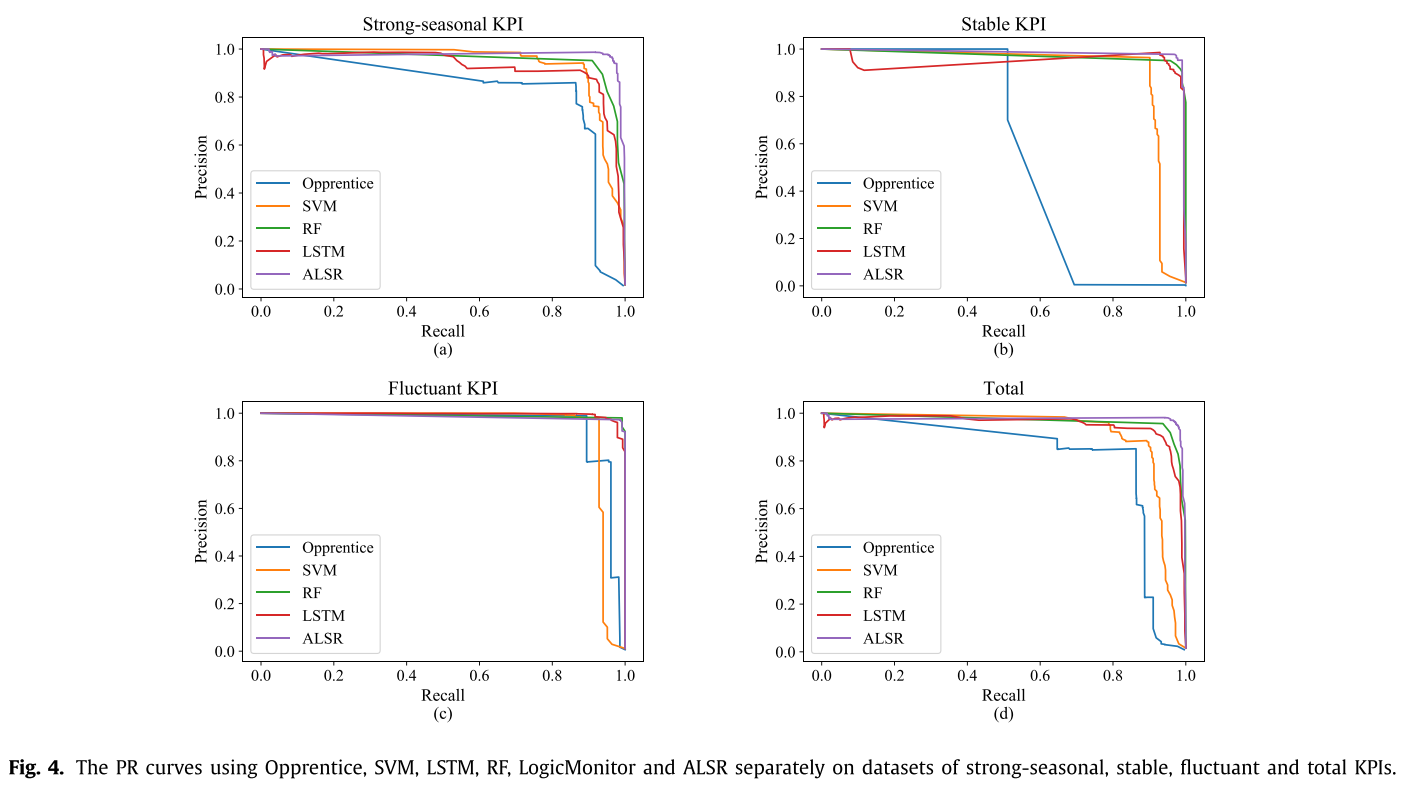
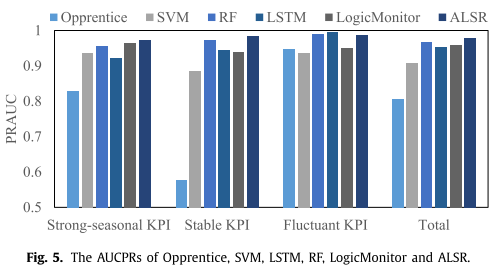
F1
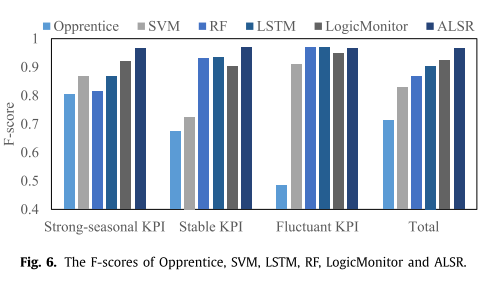
Remark
- 这篇文章的Label Screening方法实际上是在处理样本分类难易度的问题,将异常区间内容易的样本去除了
- 对于时间序列的异常检测问题,我们的目标一般是Point-based的异常标签,一个时间点的特征是有限的。如果用窗口的方式,以\(\{x_{t-w+1},\cdots,x_t\}\)作为时间\(t\)的输入(当然每个\(x_t\)可以有多个Channel),然后把预测结果作为时间\(t\)的输出
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-SA 4.0 协议 ,转载请注明出处!